Urology
The Department of Urology at Wecare Securex Cliniques delivers advanced and specialized urological care at par with international standards. The urologists are experts in treating patients with the latest and updated laparoscopic and laser technologies. The team of urologists is highly specialized in treating patients of all ages and gender with utmost and personalized care. The Department demonstrates the best example of human skill and technology as it operates with innovative technologies by performing minimally invasive procedures which in turn bring out the best results in the patient recovery.
The department provides a full spectrum of diagnostics and treatment for;
- Sharp pain in the groin region and side areas
- Signs of blood while passing urine (hematuria)
- Frequent nausea and vomiting
- Pus observed in urine
- Passing less amount of urine
- Burning and itching sensation when passing urine
- The frequent feeling of urination
- Sometimes, the occurrence of fever/chills
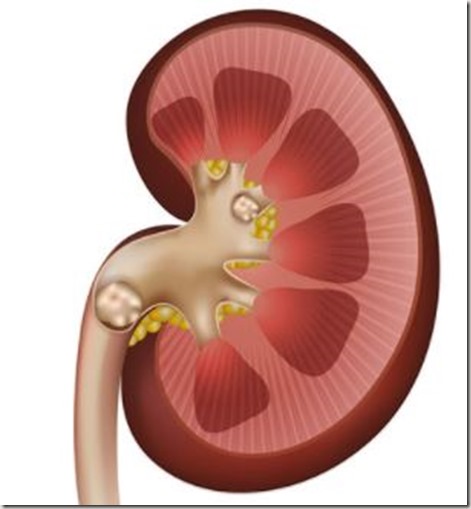
Urinary / Kidney Stone
Kidney Stones Causes :
The primary cause behind kidney stone is the lesser content of water in the body.
In short, people who drink less water on a daily basis have major threats of getting kidney stones. It is thus recommended that you should drink at least 2-3 litres of water in a day.
A kidney stone can be a result of certain diseases like Crohn’s disease, Renal Tubular Acidosis, Dent’s disease etc. People undergoing chemotherapy also have possibilities of suffering from kidney stones.
When the body lacks an adequate amount of water that is required for the dilution of uric acid, the urine gets acidic.When urine gets excessively acidic, it leads to the formation of kidney stones.
Kidney Stones Signs and Symptoms :
In general, kidney stones show no symptoms until they move into the Ureter. Once these stones enter the Ureter, the following symptoms are usually seen.
Sharp pain in the groin region and side areasSigns of blood while passing urine (hematuria)Frequent nausea and vomitingPus observed in urinePassing less amount of urineBurning and itching sensation when passing urineThe frequent feeling of urinationSometimes, the occurrence of fever/chills
Kidney Stones Diagnosis and Testing :
If your doctor observes the symptoms related to kidney stones problems, he/she may advise you a few diagnostic tests and procedures such as following:
Blood Tests : These tests inform about the presence of too much calcium or uric acid in your blood. It helps doctors to check the health of your kidney.Urine Testing : Doctor may advise you to have two urine collections for two consecutive days to assess the amount of stone forming minerals present in your urine. Imaging : Imaging tests may include simple abdominal X-rays, CT Scan and ultrasound to reveal the presence of kidney stones in your urinary tract. One advanced test is intravenous urography where a dye is injected into an arm vein and x-rays or CT images are taken as dye travels through kidney and bladder. Analyzing passed Kidney Stones : You will pass urine through a strainer so kidney stones passing through urine can be collected and analyzed in a lab.
Kidney Stone Patients FAQ to Ask Doctor :
How do doctors remove my kidney stone at Wecare Healthcare associated Hospital?
The first step is to diagnosis that involves a series of blood tests, Urinalysis, KFT, ultrasound, abdominal X-ray etc.
After diagnosing the disease, analyzing the stage of the disease and risk factors associated, the specialists here advise the right treatment.
If the problem is caught early and doctors do not find it alarming, they can prescribe ways, so stone passes down easily, naturally. Another effective method that does not involve invasive surgery is performing laser treatment of the kidney stone.
If the problem is more critical, doctors can advise different modes of treatment depending upon the condition of the patient and stone.
Drinking Enough Water / Fluid: The key to flush stones through urine is to drink at least 2-3 liters water.
Medications: Doctors may prescribe certain pain relievers to ease the pain and other medications to break and dissolve stones. Antibiotics are advised to counter infections.
Severe pain Blood in urine A strong urge to urinate Difficulty passing urine A burning sensation while urinating Nausea/Vomiting Fever/Chills
he first step is to diagnosis that involves a series of blood tests, Urinalysis, KFT, ultrasound, abdominal X-ray etc.
After diagnosing the disease, analyzing the stage of the disease and risk factors associated, the specialists here advise the right treatment.
If the problem is caught early and doctors do not find it alarming, they can prescribe ways, so stone passes down easily, naturally. Another effective method that does not involve invasive surgery is performing laser treatment of the kidney stone.
If the problem is more critical, doctors can advise different modes of treatment depending upon the condition of the patient and stone.
Enlarged Prostate
The prostate gland doubles in size at the onset of puberty and again starts to grow at the age of around 45 years. From then on it continues to grow.
In some people, it may enlarge to an abnormal extent and be referred to as an enlarged prostate. Many doctors are of the opinion that the regular and normal hormonal changes that occur in the body may be a cause of the disease.The changes that occur in the body as men get older and that is associated with the balancing of the sex hormones may specifically cause the condition. But the more exact causes are not known.
BPH (Enlarged Prostate) Symptoms:
There are a number of symptoms related to the enlargement of the prostate gland which clearly indicate the presence of the condition. These symptoms may also worsen gradually over a period of time if the disease is not treated early.
Some of the Symptoms of BPH (Enlarged Prostate) Include:
Nocturia or increased urination frequency during the night
Frequent and urgent need of urination during the day
Difficulty in starting urination
A urine stream that starts and stops abruptly
A weak stream of urine
Difficult incomplete urination or thorough emptying of the bladder
Dribbling at the end of urination
As said earlier, the enlargement of the prostate gland may also pose problems to other organs including the kidneys. There are also certain other symptoms of BPH (Enlarged Prostate) but these are less common and include:
An Infection in the urinary tract
Urine containing blood
A complete inability towards urination
Below are the most common risk factors for BPH –
BPH has been found to run in families, which means that if you have a family relative affected by the condition you are more likely to have it.
Age is another risk factor of BPH and one-third of men in between the ages 40 to 60 years may have moderate to mild symptoms. Around half the male population at the age of 80 and above has the symptoms of BPH.
Diseases including heart disease and diabetes may increase the risk of BPH.
Those having higher body mass index (BMI) or suffering from obesity are more exposed to the risk of BPH while those who exercise regularly have a reduced risk.
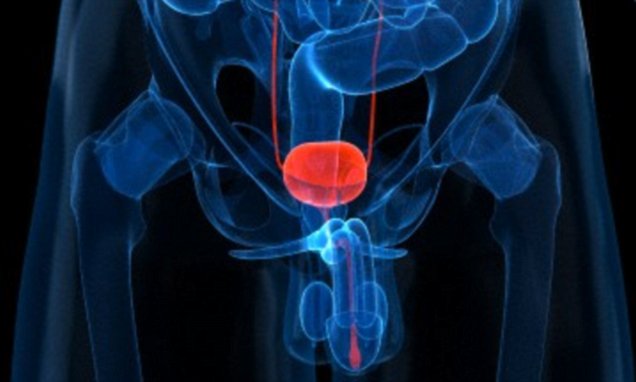
When to see your doctor for BPH (Enlarged Prostate)?
An enlarged prostate (bph) is mostly having the symptoms related to difficulty in urination, as stated earlier. It is important to see the doctor if you have any of the symptoms as these will worsen over time and may also impact the health of other organs that are part of the urinary system.
As the symptoms of BPH / enlarged prostate are similar to other grave and fatal diseases, it is very important for you to reach out to an expert to diagnose the condition in the best way and with most reliable results. A grave or more complete obstruction of the urinary tract may also occur if the condition is not treated in time.
BPH (Enlarged Prostate) Complications:
The disease may have serious and grave complications later on;
Urinary Retention – When the patient has a complete inability towards urinating, the urine gets accumulated inside the bladder and a catheter may be used for draining it out of the body. Surgery may also be done to improve the condition.
Frequent UTIs – If the urine is not adequately drained, frequent infections of the urinary tract may occur. A part of the prostate gland may be removed through surgery if infections are occurring frequently.
Kidney Damage – Damage to kidneys may also occur because of the increased pressure in the bladder due to retention of urine. The infections of the bladder may also reach the kidneys.
BPH (Enlarged Prostate) Treatment:
The severity of symptoms of BPH, shape, and size of the prostate / other organs, the age of the patient, overall health and other aspects are carefully evaluated to decide the best course of treatment. Some patients have very mild symptoms so that they do not bother much and these patients may wait a while and see how it actually goes.
Lifestyle Changes:
For very mild symptoms, lifestyle changes may be adequate in some cases. Patients are advised certain exercises that can strengthen the muscles of the pelvic floor area. They should also drink and consume less alcohol and caffeine and should avoid fluids at the time they go to sleep.
Medications:
Medicines can be used for treating the moderate to mild prostate enlargement condition. The medications can directly shrink the prostate so that it assumes a more normal size. Some medications also relax the bladder and the urethra so that urination is more comfortable.
Surgical Procedure and Techniques:
When medications and lifestyle changes do not work, surgery is the only resort available to the physician. The new minimally invasive surgical procedures ensure that no large cuts are made to the body, and these can be carried out through probes and scopes.
TUMT (TransUrethral Microwave Therapy) – Use of cold and heat for killing excess prostate cells and tissues. A catheter is entered inside the prostate and has instruments for generating and delivering microwave heat/energy.
TUNA (TransUrethral Needle Ablation) – A Cystoscope (a surgical and visual instrument is inserted via the penis into the urethra. Tiny radio-frequency (RF) needles are also passed through the Cystoscope and these deliver heat and cause necrosis, thereby shrinking the prostate issues.
Procedures including Laser Therapy and TransUrethral Resection of Prostate (TURP) are more involved surgical procedures and are carried out to remove a part of the prostate gland.
Laser Therapy – A scope is inserted via the penis tip into the urethra. As the urethra is surrounded by the prostate gland, the heat/energy (passed through the scope subsequently) cuts the excessive tissues of the prostate or melts them.
TUIP (Transurethral Incision of Prostate) – The method involves making some small incision on the prostate so that the pressure on urethra can be released.
The size of the prostate may also be managed through medications and surgical procedures. A doctor will better diagnose the condition, the extent of enlargement, and will help you choose the right course of treatment.

Ureteric Stricture:
Ureteric Stricture:
Ureteral stricture is a narrowing of the lumen of the ureter, the duct that carries urine from the kidneys to the bladder, resulting in an obstruction. Ureteral stricture may arise from a variety of causes and is characterized as either anastomotic or nonanastomotic, depending on how they develop. They may be benign or malignant.
Who get it?Any individual undergoing treatment such as an ureteroscopy for kidney, ureteric stone management or urinary diversion is at great risk for developing ureteral stricture.
Ureteric Stricture Causes
Ureteral stricture may be caused by external trauma or may develop after treatment for another condition. Ureteral stricture may be inflammatory due to gonorrhea, tuberculous uretritis, or schistosomiasis, or a rare complication of cancer.
Non-anastomotic ureteral stricture may develop after stone impaction or upper urinary tract endoscopy, as well as following pelvic radiation therapy and a variety of open and laparoscopic surgical procedure or other trauma. Anastomotic ureteral stricture may develop as a result of urinary diversion surgery.
Ureteric Stricture Symptoms
Symptoms of ureteral stricture may include pain, loin lump , flank tenderness, and/or urinary tract infection.
Diagnosis of Ureteric Stricture
It is diagnosed by IVU (IntraveneousUrogram) or retrograde urethrogram to determine the site and degree of stricture.
Ureteric Stricture Treatment
There are a variety of minimally invasive treatments for patients with ureteral strictures. A doctor may perform balloon dilation as a first step in treatment, particularly in patients who have nonanastomotic strictures.
For ureteral strictures that do not respond favorably to dilation alone, endoscopic incision is the procedure of choice for most patients. Endoscopic incision of the stricture can be performed or a laser may be used with a rigid or flexible ureteroscope. A stent may be left in place to keep the ducts open for approximately 6 weeks.
New technique called Holmium Laser Endoureterotomy is now available that may allow long-term relief from ureteral stricture if other techniques are unsuccessful.
Urethral Stricture
The urethra is one of the organs of the urinary tract that carries urine from the bladder so that it can be released from the body. The urethra tube is usually wide enough for the urine to flow easily through it. However, when the urethra tube gets contracted, it deliberately blocks down or restricts the urinary flow. This condition is known as the urethral stricture.
Causes of Urethral Stricture
Urethral stricture generally occurs due to the presence of a scar tissue or tissue inflammation. There are many possible factors for scar tissue.
For example; teens who have undergone hypospadias surgery to correct an underdeveloped urethra or men who have penile implants are prone to developing urethral stricture. Other possible causes include:
Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia (BHP)
Prostate surgery
Radiation
Catheter insertion
Pelvic fractures
Sexually Transmitted Diseases (STDs)
Risk Factors for Urethral Stricture
Some men are prone to develop a urethral stricture, especially those who have;
One or more STIs
An enlarged prostate
Urethritis
A recent catheter replacement
Symptoms of Urethral Stricture
Urethral stricture is not considered a serious issue but it can cause several symptoms, ranging from moderate to severe. It is recommended to undergo urethral stricture treatment before it gets too late.
Frequent and sudden urge to urinate
Reduction in urine volume or weak urine flow
Feeling the bladder is still full after urination
Frequent stopping and starting of urine stream
Burning sensation or pain while urinating
Incontinence (lack of control over urination)
Pain in the lower abdominal area or pelvic
Urethral discharge
Penile pain and swelling
Presence of blood in urine or semen
Darker urine color
Diagnosis of Urethral Stricture
Doctors at RG Stone follow neat procedures and several approaches for diagnosing urethral stricture.
Reviewing your medical history and symptoms
Physical examination of the penis area. Possibly looking for urethral discharge (redness)
Conducting several tests including measuring the urine rate of flow
Blood and urine test
Cystoscopy
Tests for gonorrhea and chlamydia
Urethral Stricture Treatment
The doctors at RG Stone will only prescribe the treatment option considering the severity of the condition.
1. Nonsurgical:
The doctor will use a medical instrument known as the dilator for making the urethra wider. It is done by inserting a wire into the urethra to the bladder and dilates it.
Another nonsurgical treatment option is permanent urinary catheter placement. But it has side effects as it causes urinary tract infections and bladder irritation.
2.Surgery:
Open urethroplasty is a preferred surgical option for the doctors for urethral strictures. This process involves removing the contracted tissue and reconstructing the urethra.
3.Urine Flow Diversion:
In some cases, the doctors follow urinary diversion procedures to treat the strictures. This surgery leads to the flow of urine permanently rerouted towards a small opening in the abdomen.
Kidney Cancer
Prostate Cancer
Urinary Bladder Cancer
Erectile Dysfunction
Male Infertility
